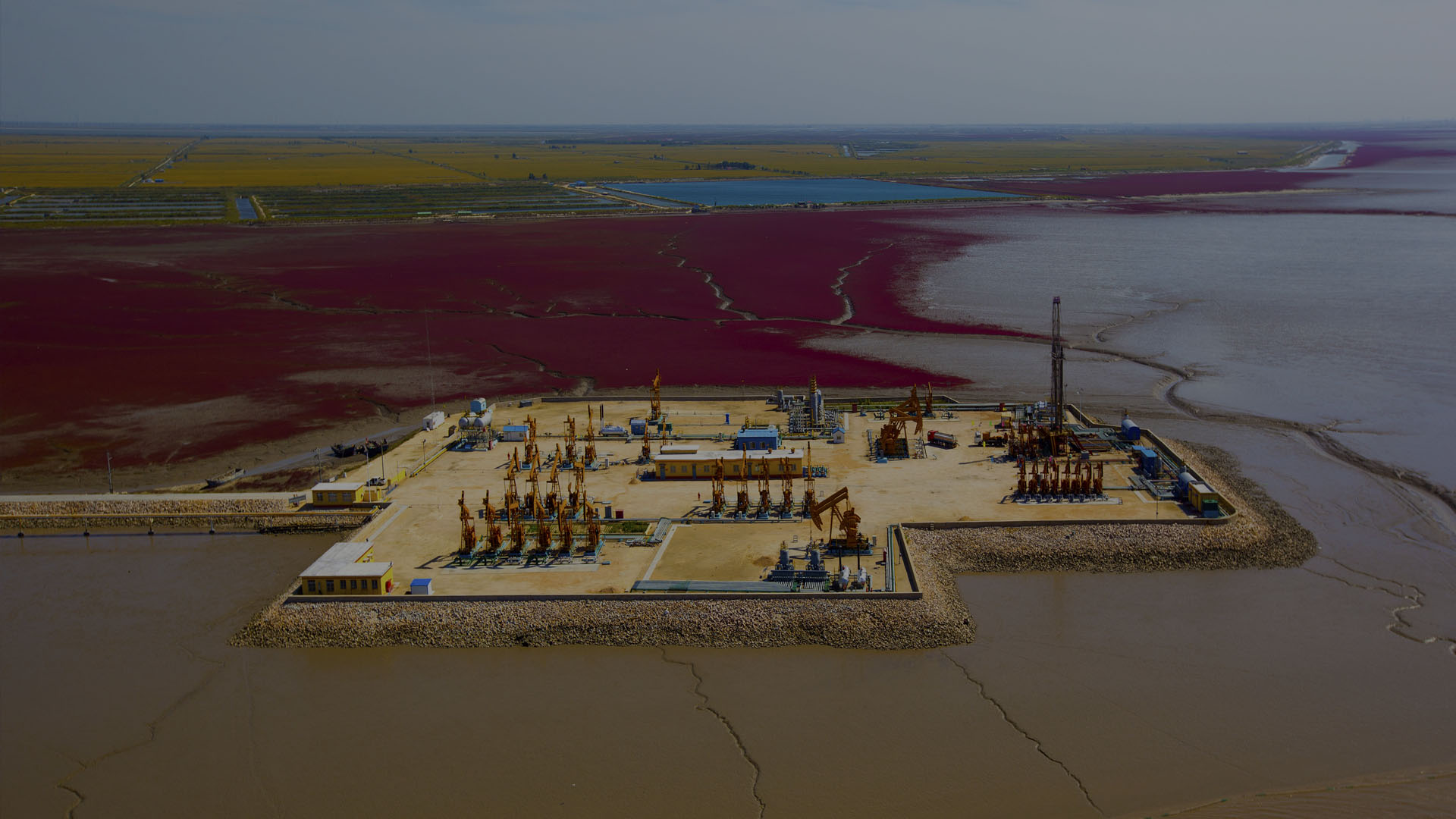
Gelling Agents
GUAR GUM is a natural galactomannan polysaccharide obtained from grinding the endosperm of the legume Cyamopsis tetragonolobus, an annual plant which grows mainly in arid and semiarid regions of India. Guar gum is available in a fast-hydrating form and is used in various oil field applications. In fracturing applications, Guar Gum functions as a friction reducing and gelling agent. Guar is easily crosslinked using a metal ion based crosslinking agent. The crosslinked fluid produces high viscosity capable of transporting high concentrations of proppant deep into the fracture. Adjustments to the crosslink viscosity help control the dimensions and growth of the fracture.

Guar Gum is also used extensively in the food industry. Applications in the food industry require gel characteristics that vary in viscosity and texture. This requires knowledge of the conditions necessary for gelling of a particular hydrocolloid dispersion. The characteristics of the gel produced and the texture it confers are particularly important aspects for the design of a specific food formulation. The most common gums found in food as gelling agents include alginate, pectin, carrageenan, gellan, gelatin, agar, modified starch, methyl cellulose and hydroxypropylmethyl cellulose.

